Due to their excellent properties, such as lightweight, high strength, and corrosion resistance, composite materials are widely used in aerospace, automotive manufacturing, and electronic equipment. As a key piece of equipment for composite material molding, the technical design of the hydraulic press directly determines the quality and performance of the composite material products. This article will delve into the key technical design aspects of composite material molding hydraulic presses from multiple perspectives, including structural design, hydraulic system design, temperature control system design, and intelligent control design.
Table of Content
- Structural Design
1.1 Overall Frame Structure
1.2 Mold Installation and Replacement Design - Hydraulic System Design
2.1 Hydraulic Principles and Pressure Control
2.2 Flow Control and Motion Speed Regulation - Temperature Control System Design
3.1 Heating Method and Heat Source Selection
3.2 Temperature Uniformity Control and Temperature Sensor Placement - Intelligent Control Design
4.1 PLC Control System
4.2 Intelligent Algorithms and Adaptive Control
1. Structural Design
1.1 Overall Frame Structure
Composite material molding hydraulic presses typically employ a three-beam, four-column structure. This structure offers high rigidity and stability, capable of withstanding significant pressure and deformation. The upper beam, movable beam, and lower beam are connected by four columns, forming a closed frame. The upper beam supports the main hydraulic cylinder. The movable beam moves up and down under the action of the main hydraulic cylinder to achieve pressure molding of the composite material, and the lower beam provides the work surface for placing the mold and composite material.
The design of the three-beam, four-column structure requires careful consideration of the strength and rigidity of each component. The columns are usually made of high-strength alloy steel and undergo heat treatment to improve their overall mechanical properties. The upper and lower beams are either cast integrally or welded, with internal reinforcing ribs to enhance rigidity. Guiding devices, such as bronze bushings or linear guides, are used between the movable beam and the columns to ensure smooth and vertical movement of the movable beam, reducing friction and wear.
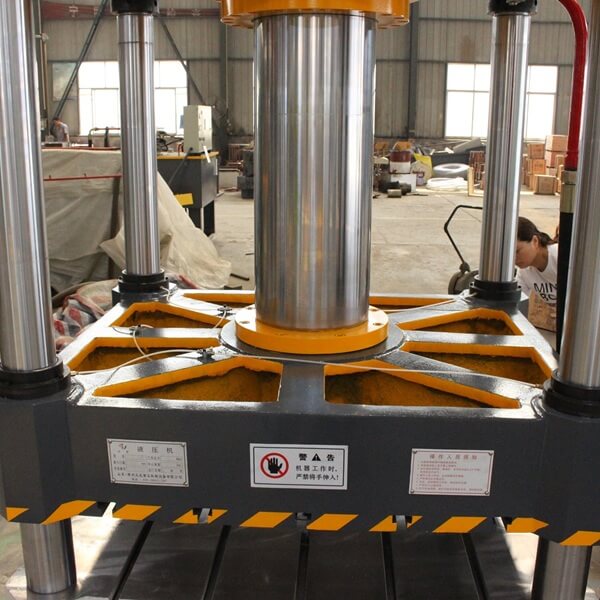

1.2 Mold Installation and Replacement Design
To accommodate the molding requirements of composite products of different shapes and sizes, the hydraulic press must be capable of quick mold replacement. The mold installation structure should be simple, convenient, and reliable. Bolt connections or quick-clamping devices are typically used. Mold mounting positioning holes and guide grooves are provided on the movable beam and lower beam to ensure accurate alignment of the mold during installation. Additionally, lifting devices or tracks can be installed around the hydraulic press to facilitate mold handling and installation.
Furthermore, the mold design must be compatible with the hydraulic press’s structure. The mold should have sufficient strength and rigidity to withstand the pressure and temperature changes during the hot pressing process. The mold cavity surface should be highly smooth and precise to ensure the composite product’s surface quality. The mold should also incorporate appropriate venting and overflow structures to prevent the formation of bubbles and defects during the molding process.

2. Hydraulic System Design
2.1 Hydraulic Principles and Pressure Control
The hydraulic system is the core component of a composite material compound molding press. Its function is to provide the hydraulic press with the necessary pressure and power. The hydraulic system typically uses a pump-accumulator drive system. A high-pressure oil pump delivers hydraulic oil to an accumulator to store energy. Then, when needed, control valves distribute the hydraulic oil to the main hydraulic cylinder and other actuators to achieve the pressurized molding of composite materials.
Pressure control is crucial in hydraulic system design. To ensure the composite material is subjected to uniform pressure during the molding process, the hydraulic system should have precise pressure regulation and stable control. Proportional relief valves or servo valves are used to achieve precise pressure regulation. Pressure sensors continuously monitor the hydraulic cylinder’s pressure and feed the signal back to the control system. The control system adjusts the proportional relief valve or servo valve based on the set pressure, maintaining the hydraulic cylinder pressure within the set range. At the same time, to reduce the impact of pressure fluctuations on molding quality, the hydraulic system should also include pressure buffering devices, such as accumulators, to absorb pressure shocks and fluctuations.

2.2 Flow Control and Motion Speed Regulation
In addition to pressure control, flow control is also a crucial aspect of hydraulic system design. The speed of the hydraulic press’s moving beam during its upward and downward movements must be adjusted to meet the molding process requirements. During the mold closing phase, rapid movement is required to shorten the production cycle. During the pressurization and holding phases, slow movement is necessary to ensure sufficient flow and curing of the composite material. During the mold opening phase, rapid movement is also required to improve production efficiency.
To adjust the moving beam’s speed, variable-displacement pumps or throttle valves in the hydraulic system control the flow rate of hydraulic oil. Variable-displacement pumps can automatically adjust displacement to meet system needs, providing stepless flow control. Throttle valves control the flow rate by changing the flow area of the throttling orifice. Furthermore, to further improve the accuracy and stability of motion speed regulation, a servo control system can be employed. By using a servo motor to drive the hydraulic pump, precise control of flow rate and pressure can be achieved.
3. Temperature Control System Design
3.1 Heating Method and Heat Source Selection
Composite material hot pressing molding requires specific temperature conditions to soften, flow, and cure the resin matrix. Therefore, the temperature control system is a crucial component of a hydraulic press for composite material hot pressing molding. Common heating methods include electric heating, oil heating, and steam heating.
Electric heating offers advantages such as fast heating speed, high temperature control accuracy, and ease of automation, but it has relatively poor heating uniformity and high energy consumption. Oil heating, on the other hand, provides uniform heating and good temperature stability, but it has a slower heating speed and requires an oil heater and a circulating oil circuit. Steam heating is suitable for large-scale production, with lower heating costs, but it has relatively lower temperature control accuracy and requires equipment such as a steam boiler.
In practical design, the appropriate heating method and heat source should be selected based on the molding process requirements and production scale of the composite material. For small-batch, high-precision composite material product molding, electric heating can be used. For large-scale production, oil heating or steam heating methods can be employed.

3.2 Temperature Uniformity Control and Temperature Sensor Placement
Temperature uniformity is one of the key factors affecting the quality of composite material products. During hot pressing, if the temperature of different parts of the mold is inconsistent, it leads to different curing rates across the composite material, resulting in internal stress and deformation and affecting the dimensional accuracy and mechanical properties of the product.
To achieve uniform temperature control, it is necessary to rationally design the heating device and the placement of temperature sensors. The heating device should use a zoned heating method, dividing the heating area into multiple zones based on the mold’s shape and size. Each zone should have independent control of heating power to ensure uniform temperature throughout each area. Temperature sensors should be evenly distributed across critical areas of the mold, including the cavity surface and the interior of the heating plate, to monitor temperature changes in real time and feed the signals back to the temperature control system. The temperature control system adjusts the heating power of each heating zone based on feedback from temperature sensors, keeping each part of the mold within the set temperature range.

4. Intelligent Control Design
4.1 PLC Control System
With the development of industrial automation technology, hydraulic presses for composite material hot pressing are increasingly using programmable logic controllers (PLCs) for control. PLC control systems offer advantages such as high reliability, flexible programming, and easy expandability, enabling precise control and real-time monitoring of parameters, including pressure, temperature, and the hydraulic press’s movement speed.
In the PLC control system, various process actions of the hydraulic press, such as mold closing, pressurization, pressure holding, and mold opening, are implemented by writing control programs. At the same time, the PLC can be connected to a touchscreen or human-machine interface (HMI), allowing operators to set process parameters, monitor equipment operating status, and view production data through the touchscreen or HMI, achieving human-machine interaction and remote control.

4.2 Intelligent Algorithms and Adaptive Control
To improve the control accuracy and production efficiency of hydraulic presses for composite material hot pressing, intelligent algorithms and adaptive control technologies can be introduced. Intelligent algorithms, such as fuzzy and neural network control, can automatically adjust control parameters based on real-time system state and historical data, achieving optimized control of parameters such as pressure and temperature. Adaptive control technology, on the other hand, can automatically adjust the hydraulic press’s operating parameters based on the composite material’s characteristics and changes in the molding process, ensuring stability and consistency.
For example, in fuzzy control, pressure and temperature are used as input variables, and the control valve opening degree is used as an output variable. Fuzzy inference and decision-making of control parameters are achieved by establishing a fuzzy rule base. Neural network control, through training a neural network model, enables it to learn the complex nonlinear relationships in the composite material molding process, thereby achieving accurate prediction and control of parameters such as pressure and temperature.
Conclusion
The technical design of a hydraulic press for composite material hot pressing is a complex systems engineering project that involves multiple aspects, including structural design, hydraulic system design, temperature control system design, and intelligent control design. Through rational design and optimization, the hydraulic press’s performance and reliability can be improved, ensuring the quality and performance of composite material products. In the future, as materials science and automation technology continue to advance, hydraulic presses for composite material molding will become more efficient, intelligent, and environmentally friendly, providing stronger support for the development of the composite materials industry.
PDH is a famous hydraulic press factory in China that offers various hydraulic press machines and knowledge. If you have any needs, please feel free to contact us!